一、简介
- 项目主页:https://appagent-official.github.io/
- code: https://github.com/m. otgod96/AppAgent
- paper: https://arxiv.org/p. f/2312.13771.pdf
2023下半年,在openai release gpt-4v api及公开相关研究(https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.17421)后,人们开始了gpt-4v在现实tasks中落地的探索之路。其中在模拟人机交互操作领域,也出现了多个工作,如https://github.com/zzxslp/MM-Navigator,本文的AppAgent,以及Rabit的LargeActionModel等。本文介绍一下AppAgent的主要思路。
AppAgent通过定义一个简单的操作空间(tap、swipe、input、long_press),使LLMAgent可以像人一样操作APP。LLMAgent通过观察记录操作及操作结果,学习不同操作的作用,从而可以操作一个未见过的APP。作者使用AppAgent在10个不同APP上尝试了50多个任务,认为AppAgent可以胜任很多不同类型的UI交互操作任务。(Android,通过adb驱动)

二、self_explorer流程
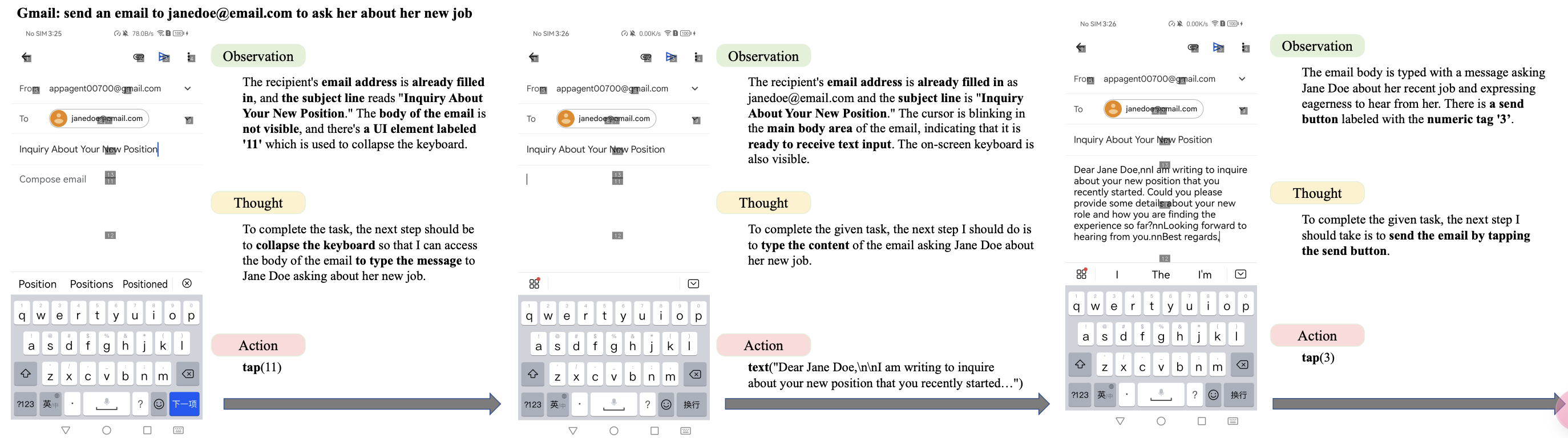
AppAgent整体上分为learn与run,learn过程为AppAgent学习思考App操作并存为Doc的过程,run可以理解为完成任务的回放过程或自动探索过程。这里简单介绍下learn过程中的self_explorer过程,其也有点类似于run中的自动探索。
给定一个Task,使AppAgent自主地在指定的App上完成此task,并记录探索的步骤,为后续Agent执行任务提供参考。self_explorer的流程(简版,部分细节不做描述)如下:
- 初始化(获取App信息、获取Device信息、获取Task信息、创建任务文件夹)
- 进入Action循环
- 获取页面元素树,整理可交互元素(ADB xml驱动)
- 在图像中标注元素 (set-of-mark)
- 页面信息 / 历史交互信息,组装Prompt,询问gpt-4v下一步该进行何种操作
- 得到gpt-4v回复,进行操作
- 获取操作后页面信息,反思并记录结果
- 重复循环,直到完成task or 达到最大步数
其中一个关键步骤为:Action选取 ,在self_explorer过程中整体的Prompt为:
You are an agent that is trained to complete certain tasks on a smartphone. You will be given a screenshot of a smartphone app. The interactive UI elements on the screenshot are labeled with numeric tags starting from 1.
You can call the following functions to interact with those labeled elements to control the smartphone:
1. tap(element: int)
This function is used to tap an UI element shown on the smartphone screen. "element" is a numeric tag assigned to an UI element shown on the smartphone screen. A simple use case can be tap(5), which taps the UI element labeled with the number 5.
2. text(text_input: str)
This function is used to insert text input in an input field/box. text_input is the string you want to insert and must be wrapped with double quotation marks. A simple use case can be text("Hello, world!"), which inserts the string "Hello, world!" into the input area on the smartphone screen. This function is only callable when you see a keyboard showing in the lower half of the screen.
3. long_press(element: int)
This function is used to long press an UI element shown on the smartphone screen.
"element" is a numeric tag assigned to an UI element shown on the smartphone screen.
A simple use case can be long_press(5), which long presses the UI element labeled with the number 5.
4. swipe(element: int, direction: str, dist: str)
This function is used to swipe an UI element shown on the smartphone screen, usually a scroll view or a slide bar.
"element" is a numeric tag assigned to an UI element shown on the smartphone screen. "direction" is a string that
represents one of the four directions: up, down, left, right. "direction" must be wrapped with double quotation
marks. "dist" determines the distance of the swipe and can be one of the three options: short, medium, long. You should
choose the appropriate distance option according to your need.
A simple use case can be swipe(21, "up", "medium"), which swipes up the UI element labeled with the number 21 for a medium distance.
The task you need to complete is to <task_description>. Your past actions to proceed with this task are summarized as follows: <last_act>
Now, given the following labeled screenshot, you need to think and call the function needed to proceed with the task.
Your output should include three parts in the given format:
Observation: <Describe what you observe in the image>
Thought: <To complete the given task, what is the next step I should do>
Action: <The function call with the correct parameters to proceed with the task. If you believe the task is completed or there is nothing to be done, you should output FINISH. You cannot output anything else except a function call or FINISH in this field.>
Summary: <Summarize your past actions along with your latest action in one or two sentences. Do not include the numeric tag in your summary>
You can only take one action at a time, so please directly call the function.
整体上,首先给大模型prefix条件,明确当前背景,再表明当前所有给予的信息,主要有页面信息,可执行操作信息,任务信息,返回的要求。其中对于页面信息:
在UI交互领域,让App页面元素变为机器可理解颗粒度的原子是一项较困难的事情,为了能让GPT-4V能够理解当前页面,以及其Action决策与页面中具体元素的coords相对应,作者使用了set-of-mark的方式,将通过UI Element Tree获取到的元素一一标号,并将标号画在原本的截图上,如下图所示:
 从而GPT-4v在返回要操作的元素时,可以直接返回元素标号,我们也可以直接根据标号去操作对应元素,打破元素信息与视觉位置的gap。
从而GPT-4v在返回要操作的元素时,可以直接返回元素标号,我们也可以直接根据标号去操作对应元素,打破元素信息与视觉位置的gap。
询问后,GPT-4V会按照要求的 Observation Thought Action Summary返回它的观察,思考,决策与总结。我们根据他的决策,去执行对应的操作。在操作后,我们得到了此次action执行后App反应的结果截图,再次进行一遍set-of-mark的过程,开始进入反思reflection:
I will give you screenshots of a mobile app before and after <action> the UI
element labeled with the number '<ui_element>' on the first screenshot. The numeric tag of each element is located at
the center of the element. The action of <action> this UI element was described as follows:
<last_act>
The action was also an attempt to proceed with a larger task, which is to <task_desc>. Your job is to carefully analyze
the difference between the two screenshots to determine if the action is in accord with the description above and at
the same time effectively moved the task forward. Your output should be determined based on the following situations:
1. BACK
If you think the action navigated you to a page where you cannot proceed with the given task, you should go back to the
previous interface. At the same time, describe the functionality of the UI element concisely in one or two sentences by
observing the difference between the two screenshots. Notice that your description of the UI element should focus on
the general function. Never include the numeric tag of the UI element in your description. You can use pronouns such as
"the UI element" to refer to the element. Your output should be in the following format:
Decision: BACK
Thought: <explain why you think the last action is wrong and you should go back to the previous interface>
Documentation: <describe the function of the UI element>
2. INEFFECTIVE
If you find the action changed nothing on the screen (screenshots before and after the action are identical), you
should continue to interact with other elements on the screen. Notice that if you find the location of the cursor
changed between the two screenshots, then they are not identical. Your output should be in the following format:
Decision: INEFFECTIVE
Thought: <explain why you made this decision>
3. CONTINUE
If you find the action changed something on the screen but does not reflect the action description above and did not
move the given task forward, you should continue to interact with other elements on the screen. At the same time,
describe the functionality of the UI element concisely in one or two sentences by observing the difference between the
two screenshots. Notice that your description of the UI element should focus on the general function. Never include the
numeric tag of the UI element in your description. You can use pronouns such as "the UI element" to refer to the
element. Your output should be in the following format:
Decision: CONTINUE
Thought: <explain why you think the action does not reflect the action description above and did not move the given
task forward>
Documentation: <describe the function of the UI element>
4. SUCCESS
If you think the action successfully moved the task forward (even though it did not completed the task), you should
describe the functionality of the UI element concisely in one or two sentences. Notice that your description of the UI
element should focus on the general function. Never include the numeric tag of the UI element in your description. You
can use pronouns such as "the UI element" to refer to the element. Your output should be in the following format:
Decision: SUCCESS
Thought: <explain why you think the action successfully moved the task forward>
Documentation: <describe the function of the UI element>
将<上一个操作描述> <交互后页面信息> <task信息> <当前reflection结果>给予GPT-4V,让其返回当前action最终的Decision Thought 与Documentation。其中反思结果会进行落库作为经验知识。反思完成后完成当前Action循环。
三、Grid模式
元素与坐标的set-of-mark对应,作者开始的实现是利用元素树,而做APP自动化有一个很大的痛点便是技术栈多种多样,不同APP元素树的组成、获取方式都不一样,仅通过Native的元素树,很容易出现元素丢失的情况,甚至在某些APP上直接不可用,于是作者更新了Grid模式,具体的描述如下:
You should call this function when you find the element you want to interact with is not labeled with a numeric tag and other elements with numeric tags cannot help with the task. The function will bring up a grid overlay to divide the smartphone screen into small areas and this will give you more freedom to choose any part of the screen to tap, long press, or swipe.
思路便是将整个页面按滑动窗口分成不同的区域(patch),每个区域有一个标号,从而有些无法用元素树标号的元素,可以通过Grid的标号来代表。用此种方式兼容了元素树缺失的情况。
四、总结
最后贴一个效果流程:
 在约束了Action Space(可操作空间),假如经验知识后,任务完成成功率可达到84.4%,接近人工水平。
在约束了Action Space(可操作空间),假如经验知识后,任务完成成功率可达到84.4%,接近人工水平。
